What is motivation?
Motivation is the external or internal drive that pushes a person to pursue goals, engage in activities, or achieve a desired outcome. It can vary greatly between individuals, depending on personal goals, values, and external influences.
Types of learning motivation
1. Integrative motivation.
Based on my understanding, integrative motivation is driven by ones' interest in learning the language in order to better understand the language and its culture. An
example of integrative motivation is students practice for their spelling test because
they are interested in increasing their vocabulary.
2. Instrumental motivation.
Instrumental motivation is where motivation
is driven by one's interest in learning the language because they want to achieve certain goals or other practical reason. For example, students practice for
their spelling test because they want the teacher to praise them and give them
presents or they want to avoid punishment from the teacher.
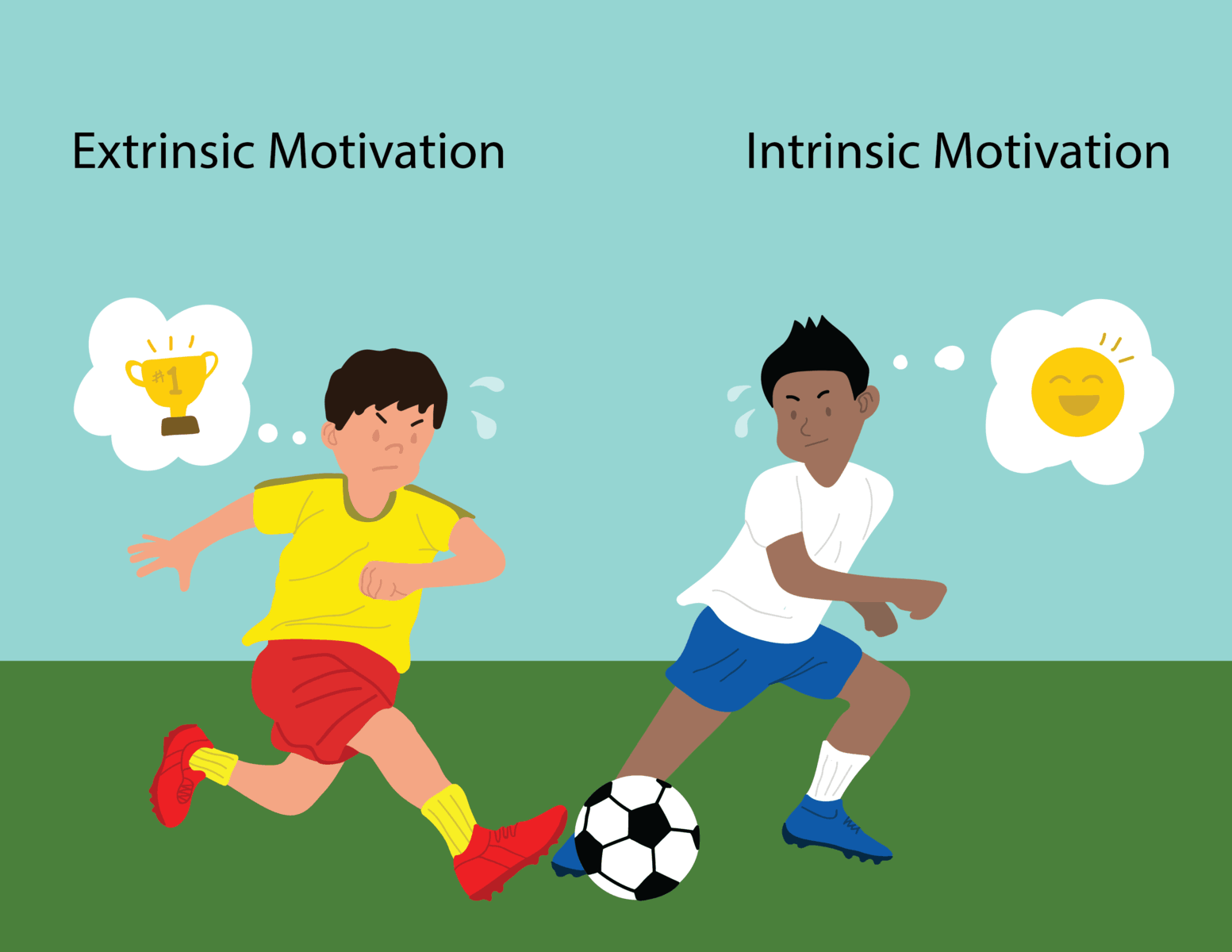
Integrative
motivation
Instrumental
motivation
Why is motivation important in the process of teaching and learning?
1. Enhancing Engagement and Participation
Motivation encourages students to actively participate in class activities, discussions, and assignments.
2. Improving Academic Performance
Motivated students tend to put more effort into their studies and are more persistent when facing challenges.
3. Developing a Growth Mindset
Motivated students often develop resilience as they see failures as opportunities to learn and improve.